Keep up with the latest news and be part of our weekly giveaways and airtime sharing; follow our WhatsApp channel for more updates. Click to Follow us
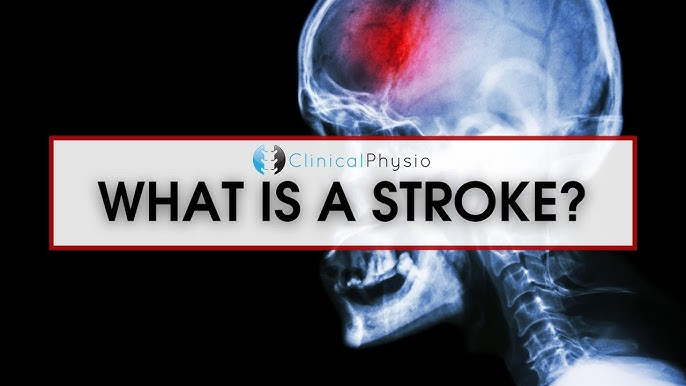
A stroke, also known as a brain attack, occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted, either due to a blockage or a rupture of the blood vessels. This can lead to damage or death of brain cells, resulting in loss of brain function. Stroke is a leading cause of death and disability worldwide, but the good news is that many strokes can be prevented by making lifestyle changes and managing underlying health conditions.
Understanding the Risk Factors
Before we dive into the ways to reduce the risk of stroke, it’s essential to understand the risk factors. Some of the most significant risk factors for stroke include:
- High blood pressure: Uncontrolled high blood pressure is the leading cause of stroke.
- High cholesterol: High levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol can increase the risk of stroke.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are at a higher risk of stroke.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of stroke.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of stroke.
- Physical inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can increase the risk of stroke.
- Family history: Having a family history of stroke increases the risk.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce the Risk of Stroke
Making lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of stroke. Here are some ways to do so:
1. Maintain a Healthy Blood Pressure
- Monitor your blood pressure regularly.
- Follow a healthy diet that is low in sodium and rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise regularly, such as walking, jogging, or cycling.
- Manage stress through techniques like meditation or deep breathing.
2. Exercise Regularly
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
- Incorporate strength-training exercises into your routine, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises.
- Increase your physical activity levels by taking the stairs, walking to work, or doing household chores.
3. Eat a Healthy Diet
- Focus on consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources.
- Limit your intake of processed and packaged foods, sugary drinks, and saturated fats.
- Incorporate healthy fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids, into your diet.
4. Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Aim for a body mass index (BMI) between 18.5 and 24.9.
- Eat a healthy and balanced diet.
- Exercise regularly.
5. Quit Smoking
- Seek professional help, such as counseling or medication, to quit smoking.
- Avoid secondhand smoke.
- Use nicotine replacement therapy, such as gum or patches, to manage withdrawal symptoms.
6. Limit Alcohol Consumption
- Drink in moderation, defined as up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.
- Avoid binge drinking.
- Choose low-risk drinking options, such as wine or beer, instead of hard liquor.
7. Get Enough Sleep
- Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
- Establish a consistent sleep schedule.
- Create a sleep-conducive environment, such as keeping the room cool, dark, and quiet.
8. Manage Stress
- Engage in stress-reducing activities, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
- Take regular breaks and practice self-care.
- Seek professional help if you’re experiencing chronic stress.
Managing Underlying Health Conditions
Managing underlying health conditions can also reduce the risk of stroke. Here are some ways to do so:
1. Manage High Blood Pressure
- Work with your healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan.
- Take medication as prescribed.
- Monitor your blood pressure regularly.
2. Manage High Cholesterol
- Work with your healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan.
- Take medication as prescribed.
- Make lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly.
3. Manage Diabetes
- Work with your healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan.
- Take medication as prescribed.
- Make lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly.
4. Get Regular Check-Ups
- Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider.
- Monitor your blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels regularly.
- Stay up-to-date on recommended vaccinations and screenings.
Conclusion
Reducing the risk of stroke requires a combination of lifestyle changes and managing underlying health conditions. By following the tips outlined in this article, you can significantly reduce your risk of stroke and maintain
Please don’t forget to “Allow the notification” so you will be the first to get our gist when we publish it.
Drop your comment in the section below, and don’t forget to share the post.







